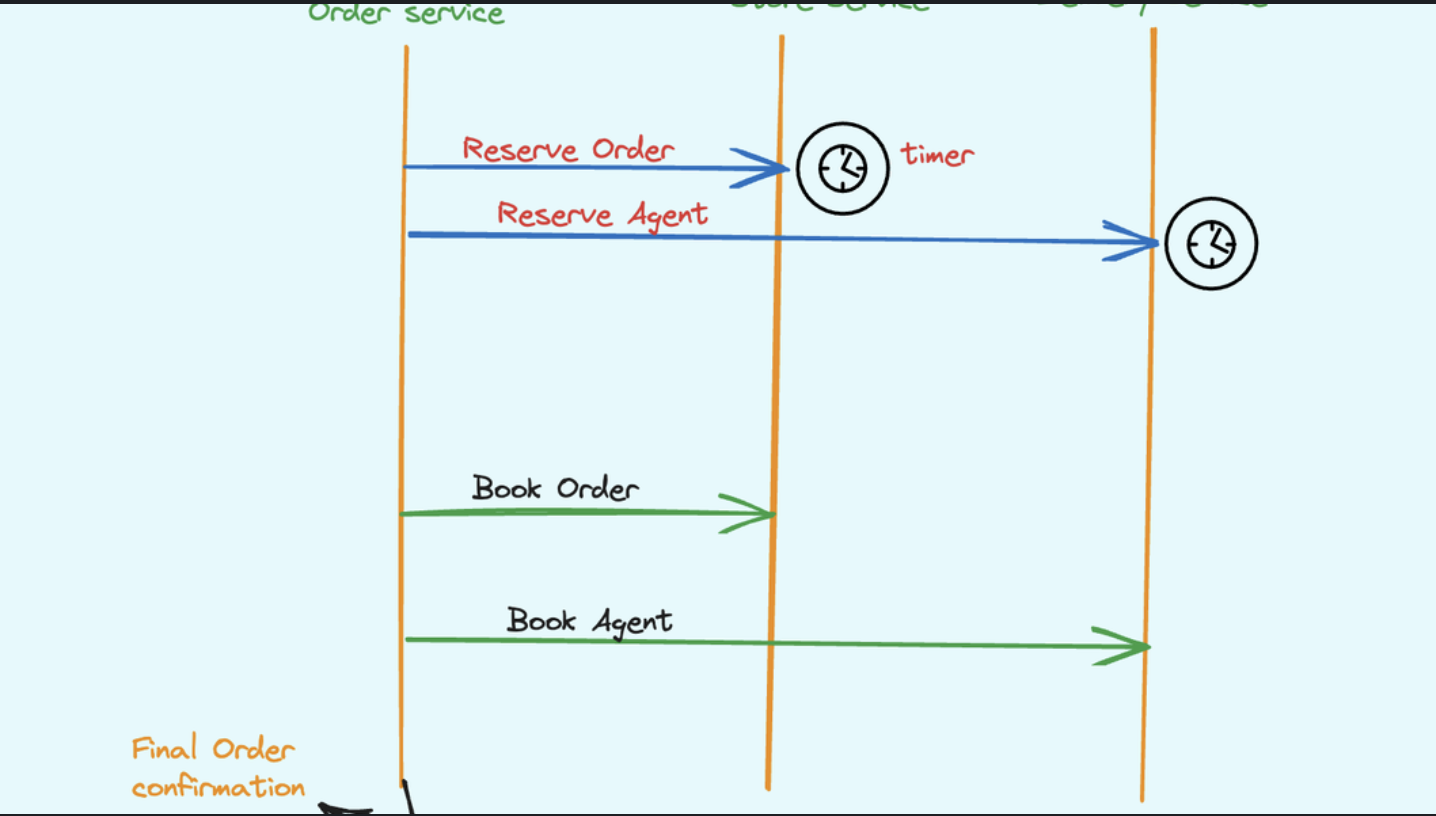
Storage mutator in a knowledge graph is a component that is responsible for updating the knowledge graph with new or changed data. It is typically implemented as a service that receives mutation requests from various sources, such as data pipelines, APIs, or user interfaces. The storage mutator then validates the mutation requests and applies them to the knowledge graph.
Storage mutators are important for keeping knowledge graphs up-to-date and accurate. They can also be used to implement complex data transformations, such as merging data from multiple sources or converting data into a different format.
One common pattern for implementing storage mutators is to use a message bus, such as Kafka. This allows data pipelines to send mutation requests to the storage mutator asynchronously, without having to wait for a response. The storage mutator can then process the mutation requests at its own pace, ensuring that the knowledge graph is always updated in a timely manner.
Another important consideration for storage mutators is idempotency. This means that the same mutation request can be applied multiple times without any negative effects. This is important because data pipelines may sometimes resend mutation requests that have already been processed.
Let’s talk about one very simple example from daily life.
Imagine you are building a knowledge graph that stores information about all the restaurants in the world. You want this knowledge graph to be as up-to-date as possible, so you need a way to update it with new or changed data. This is where a storage mutator comes in.
A storage mutator is a component that is responsible for updating the knowledge graph. It receives requests from various sources, such as data pipelines, APIs, or user interfaces, and then applies those changes to the knowledge graph.
For example, if a new restaurant opens up, a data pipeline might send a request to the storage mutator to add that restaurant to the knowledge graph. Or, if a user changes the address of an existing restaurant in the knowledge graph, the storage mutator would be responsible for applying that change.
Storage mutators are important for keeping knowledge graphs up-to-date and accurate. They can also be used to implement complex data transformations, such as merging data from multiple sources or converting data into a different format.
Here are some of the benefits of using a storage mutator in a knowledge graph:
-
Scalability: Storage mutators can be scaled to handle large volumes of mutation requests. This is important for knowledge graphs that are used to power high-traffic applications.
-
Reliability: Storage mutators are typically designed to be reliable and fault-tolerant. This means that they can continue to operate even if there are problems with some of the data pipelines or other components that send mutation requests.
-
Flexibility: Storage mutators can be used to implement complex data transformations and to update knowledge graphs from a variety of sources.
Here are some of the challenges of using a storage mutator in a knowledge graph:
-
Complexity: Storage mutators can be complex to implement and maintain. This is especially true for large and complex knowledge graphs.
-
Performance: Storage mutators can have a significant impact on the performance of a knowledge graph, especially if they are not implemented efficiently.
-
Correctness: It is important to ensure that storage mutators are implemented correctly to avoid introducing errors into the knowledge graph.
Overall, storage mutators are a valuable tool for keeping knowledge graphs up-to-date and accurate. However, it is important to carefully consider the benefits and challenges before implementing a storage mutator in a knowledge graph. 💡